Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 10: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Practice Book for KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SA Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Fluid Mechanics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
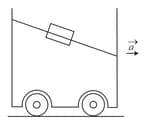
An open water tanker moving on a horizontal straight road has a cubical block of cork floating over its surface. If the tanker has an acceleration of as shown, the acceleration of the cork w.r.t. container is (ignore viscosity)
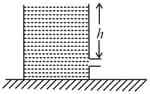
In the figure shown, a light container is kept on a horizontal rough surface of the coefficient of friction . A very small hole of area is made at depth . Water of volume is filled in the container. The friction is not sufficient to keep the container at rest. The acceleration of the container initially is
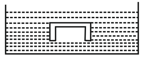
An empty glass jar is submerged in a tank of water with the open mouth of the jar downwards, so that air inside the jar is trapped and cannot get out. As the jar is pushed down slowly, the magnitude of net buoyant force on the system of volume of gas trapped in the jar and the jar:
One end of light inelastic string is tied to a helium filled balloon and its other end is tied to bottom of a water filled container at point The container lies on a fixed horizontal surface and is pulled horizontally towards right with constant horizontal acceleration of magnitude . Assuming no relative motion of balloon and water with respect to container, the string will be inclined with vertical line passing through by an angle. ( is acceleration due to gravity)
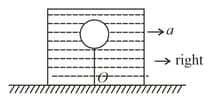
Figure shows a closed container completely filled with an ideal liquid of density . In the liquid there is a spherical body of volume and density attached to a string whose other end is attached to the roof of the container. The container is accelerating with an acceleration '' towards right. The magnitude of force exerted by the liquid on the spherical body when it is in equilibrium with respect to the liquid, will be
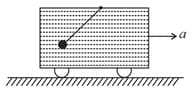
The given container is in contact with vertical wall. The container has liquid of density . There is a small hole of cross-section area of . At the given moment ground can exert maximum friction force on the container. At given instant the normal force exerted by the vertical wall on container is , find the value of .
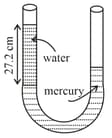
A simple open -tube contains mercury. Now water is poured slowly up to height in the left arm. How high (in ) does the mercury rise in the right arm from its initial level in equilibrium state? (Take density of mercury and that of water and )
A liquid is kept in a cylindrical vessel which is rotated about its axis. The liquid rises at the sides. If the radius of the vessel is and the speed of rotation is , The difference in the height of the liquid at the centre of the vessel and its sides will be
